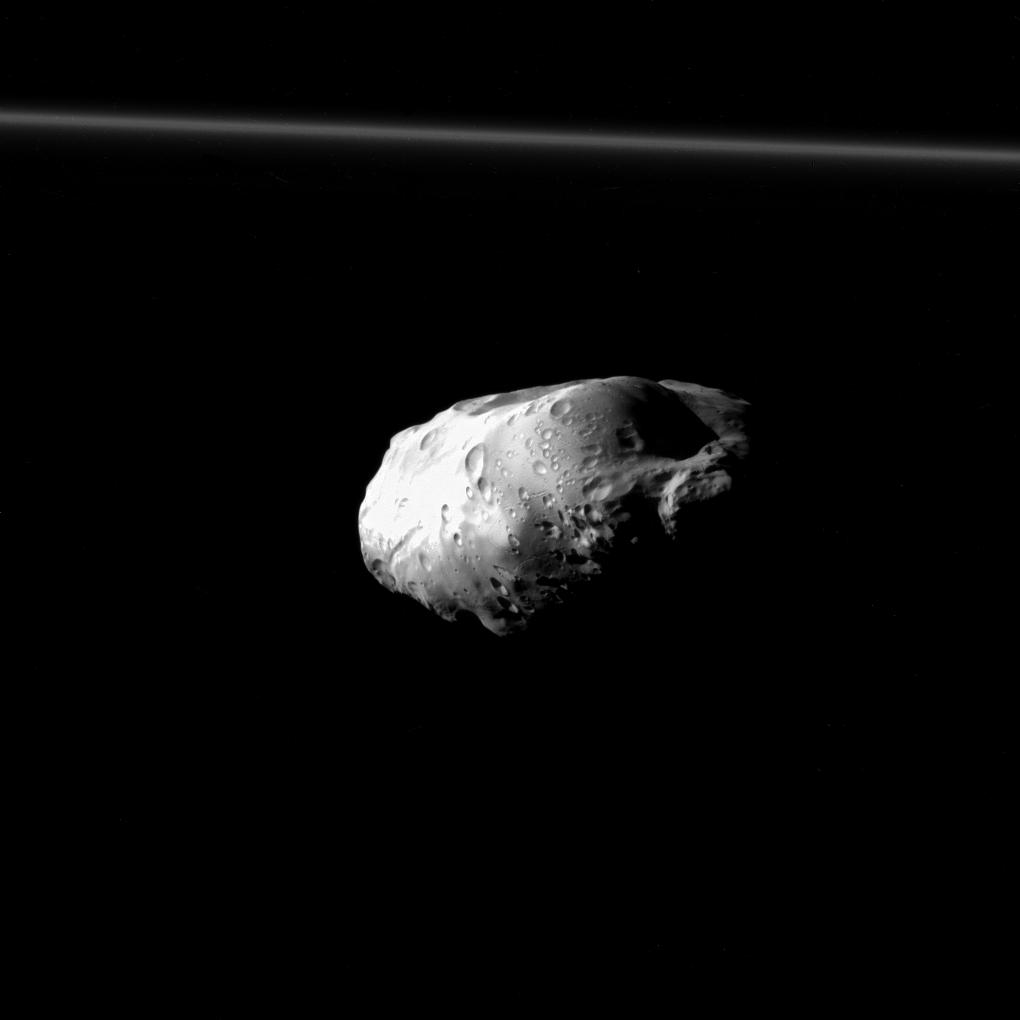
YosemiteSam
Unfriendly and Aloof!
- Messages
- 45,858
- Reaction score
- 22,195

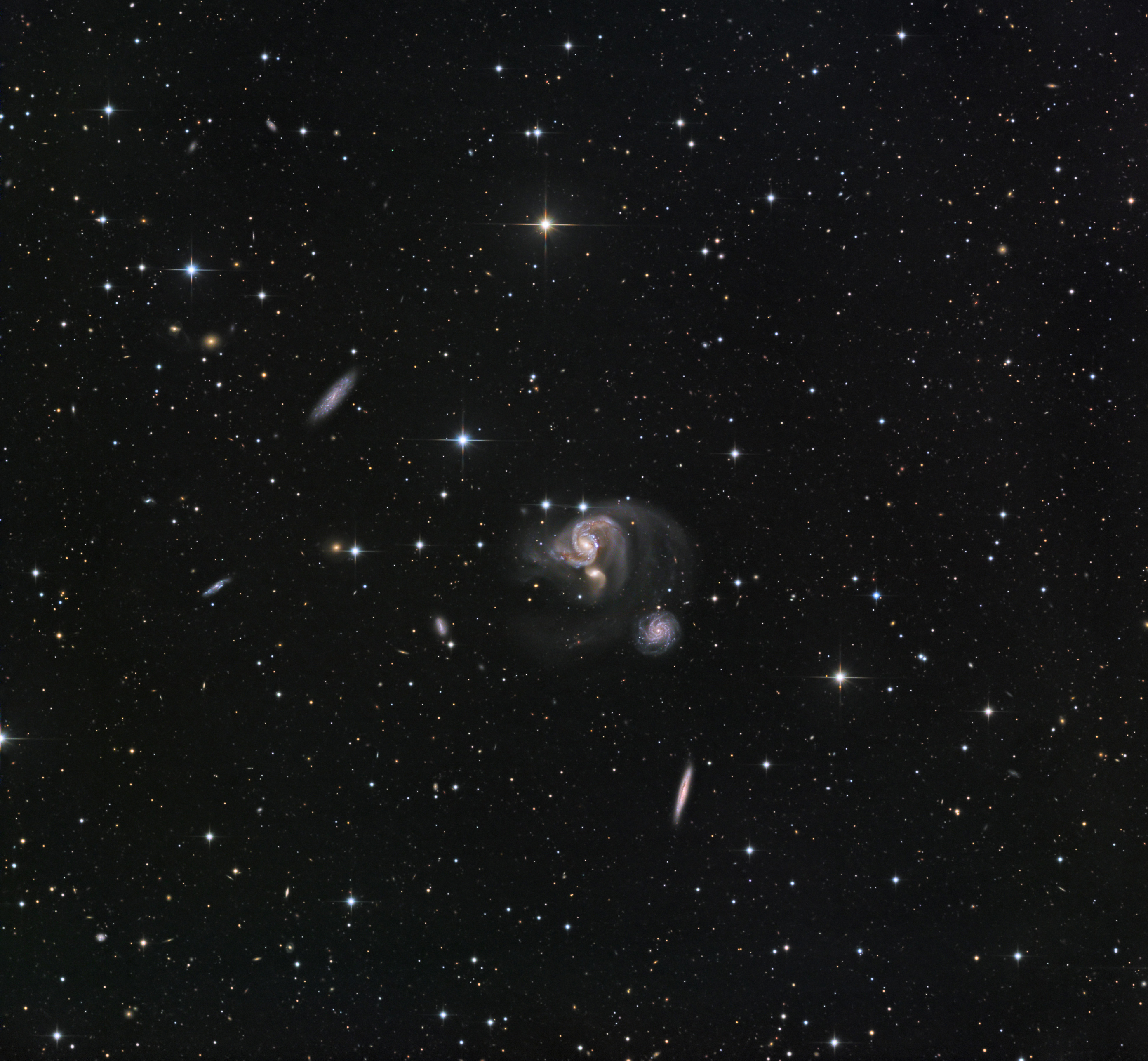
The Horsehead and Flame Nebula
The Horsehead Nebula (also known as Barnard 33 in bright nebula IC 434) is a dark nebula in the constellation Orion. The nebula is located just below (to the south of) Alnitak, the star farthest left on Orion's Belt, and is part of the much larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. The Horsehead Nebula is approximately 1500 light years from Earth. It is one of the most identifiable nebulae because of the shape of its swirling cloud of dark dust and gases, which is similar to that of a horse's head when viewed from Earth. The shape was first noticed in 1888 by Williamina Fleming on photographic plate B2312 taken at the Harvard College Observatory. The red glow originates from hydrogen gas predominantly behind the nebula, ionized by the nearby bright star Sigma Orionis. The darkness of the Horsehead is caused mostly by thick dust, although the lower part of the Horsehead's neck casts a shadow to the left. Streams of gas leaving the nebula are funneled by a strong magnetic field. Bright spots in the Horsehead Nebula's base are young stars just in the process of forming.
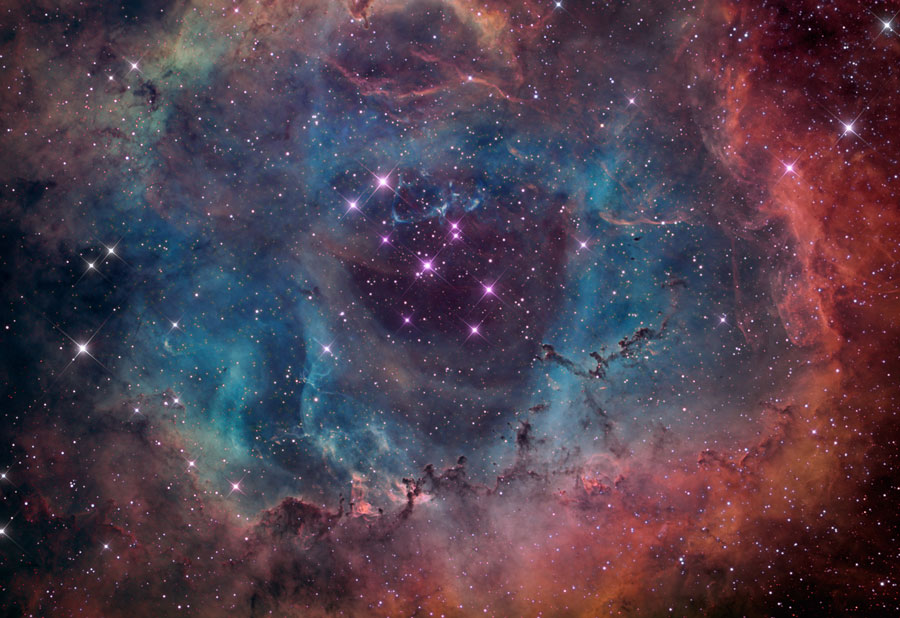
The Flame Nebula, (white leaf looking cloud formation) designated as NGC 2024 and Sh2-277, is an emission nebula in the constellation Orion. It is about 900 to 1,500 light-years away.
The bright star Alnitak (ζ Ori), the easternmost star in the Belt of Orion, shines energetic ultraviolet light into the Flame and this knocks electrons away from the great clouds of hydrogen gas that reside there. Much of the glow results when the electrons and ionized hydrogen recombine. Additional dark gas and dust lies in front of the bright part of the nebula and this is what causes the dark network that appears in the center of the glowing gas. The Flame Nebula is part of the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex, a star-forming region that includes the famous Horsehead Nebula.
At the center of the Flame Nebula is a cluster of newly formed stars, 86% of which have circumstellar disks. X-ray observations by the Chandra X-ray Observatory show several hundred young stars, out of an estimated population of 800 stars. X-ray and infrared images indicate that the youngest stars are concentrated near the center of the cluster.

The Horsehead Nebula (also known as Barnard 33 in bright nebula IC 434) is a dark nebula in the constellation Orion. The nebula is located just below (to the south of) Alnitak, the star farthest left on Orion's Belt, and is part of the much larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. The Horsehead Nebula is approximately 1500 light years from Earth. It is one of the most identifiable nebulae because of the shape of its swirling cloud of dark dust and gases, which is similar to that of a horse's head when viewed from Earth. The shape was first noticed in 1888 by Williamina Fleming on photographic plate B2312 taken at the Harvard College Observatory. The red glow originates from hydrogen gas predominantly behind the nebula, ionized by the nearby bright star Sigma Orionis. The darkness of the Horsehead is caused mostly by thick dust, although the lower part of the Horsehead's neck casts a shadow to the left. Streams of gas leaving the nebula are funneled by a strong magnetic field. Bright spots in the Horsehead Nebula's base are young stars just in the process of forming.
The Flame Nebula, (white leaf looking cloud formation) designated as NGC 2024 and Sh2-277, is an emission nebula in the constellation Orion. It is about 900 to 1,500 light-years away.
The bright star Alnitak (ζ Ori), the easternmost star in the Belt of Orion, shines energetic ultraviolet light into the Flame and this knocks electrons away from the great clouds of hydrogen gas that reside there. Much of the glow results when the electrons and ionized hydrogen recombine. Additional dark gas and dust lies in front of the bright part of the nebula and this is what causes the dark network that appears in the center of the glowing gas. The Flame Nebula is part of the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex, a star-forming region that includes the famous Horsehead Nebula.
At the center of the Flame Nebula is a cluster of newly formed stars, 86% of which have circumstellar disks. X-ray observations by the Chandra X-ray Observatory show several hundred young stars, out of an estimated population of 800 stars. X-ray and infrared images indicate that the youngest stars are concentrated near the center of the cluster.