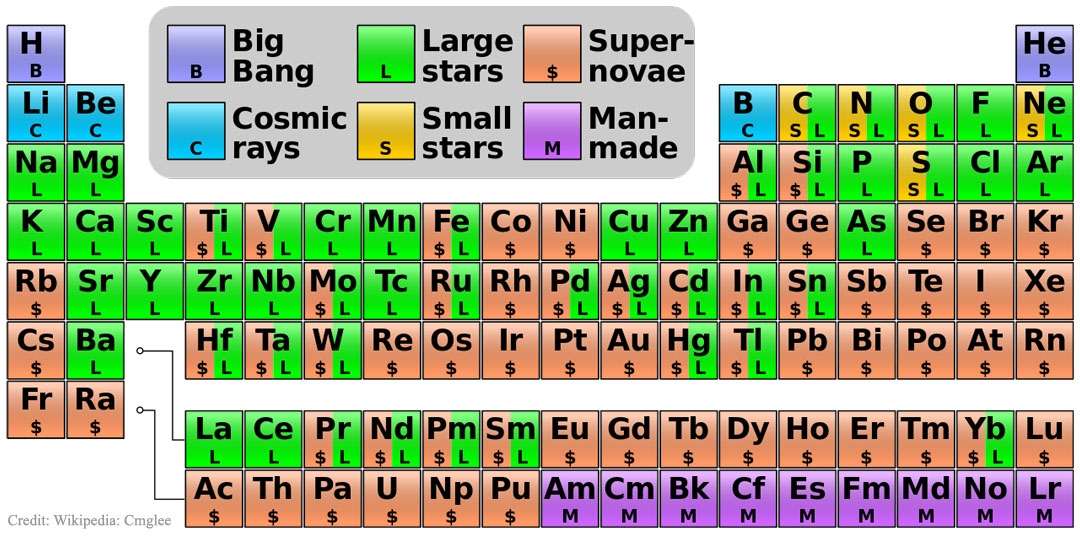
YosemiteSam
Unfriendly and Aloof!
- Messages
- 45,858
- Reaction score
- 22,195

How about another moon? (Han Solo, "That's no moon!")
I find it rather spooky that worlds like this exist and very well could have life that exists on them. On the galactic scale, any life on Enceladus would literally be in our back pocket. (Enceladus is on average 790 million miles from us)
Global Ocean Suspected on Saturn's Moon Enceladus
Image Credit: Cassini Imaging Team, SSI, JPL, ESA, NASA
Explanation: Do some surface features on Enceladus roll like a conveyor belt? A leading interpretation of images taken of Saturn's most explosive moon indicate that they do. This form of asymmetric tectonic activity, very unusual on Earth, likely holds clues to the internal structure of Enceladus, which may contain subsurface seas where life might be able to develop. Pictured above is a composite of 28 images taken by the robotic Cassini spacecraft in 2008 just after swooping by the ice-spewing orb. Inspection of these images show clear tectonic displacements where large portions of the surface all appear to move all in one direction. On the image right appears one of the most prominent tectonic divides: Labtayt Sulci, a canyon about one kilometer deep. The magnitude of Enceladus' wobble as it orbits Saturn might indicate damping by a globally extending underground ocean layer.
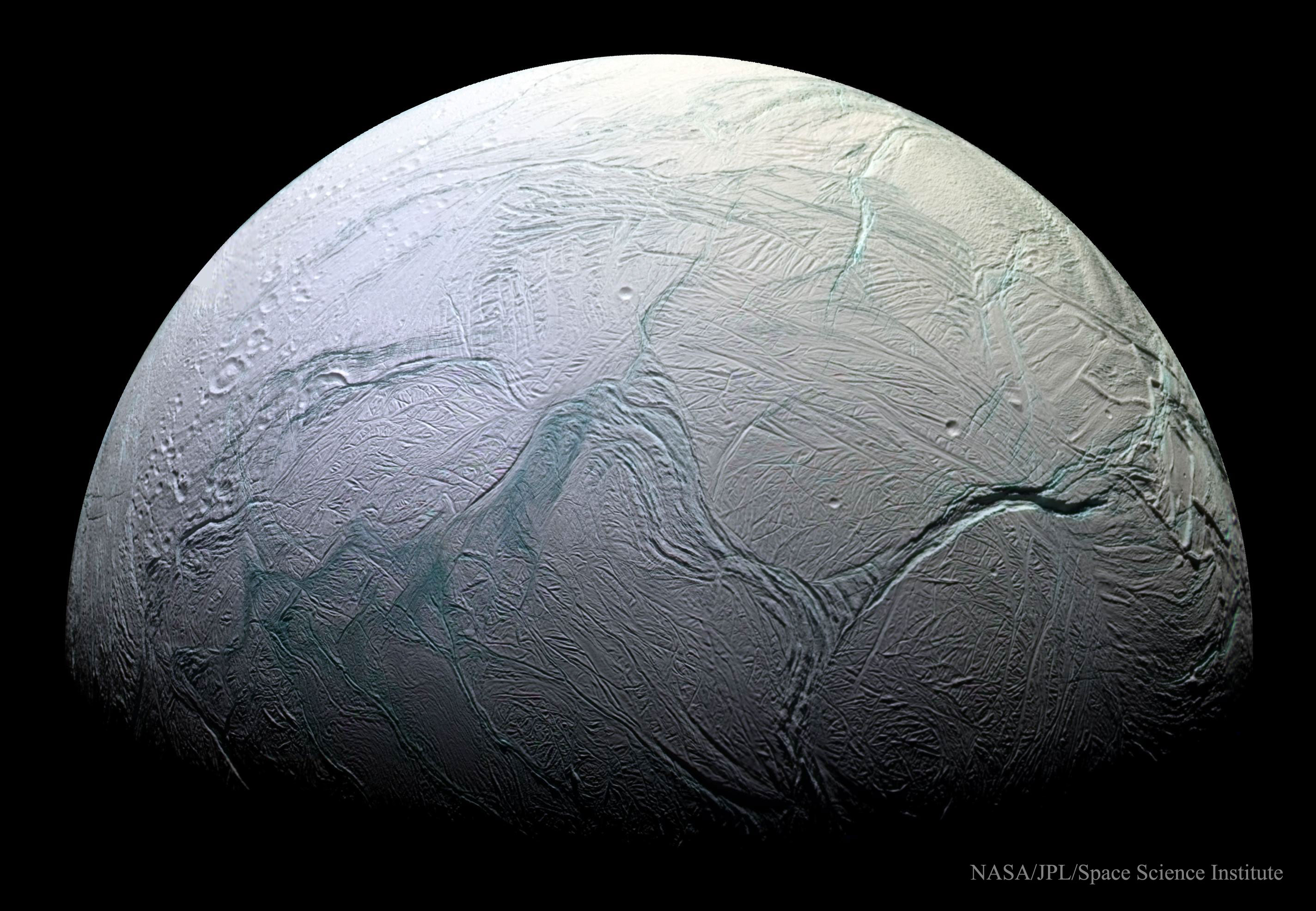

I find it rather spooky that worlds like this exist and very well could have life that exists on them. On the galactic scale, any life on Enceladus would literally be in our back pocket. (Enceladus is on average 790 million miles from us)

Global Ocean Suspected on Saturn's Moon Enceladus
Image Credit: Cassini Imaging Team, SSI, JPL, ESA, NASA
Explanation: Do some surface features on Enceladus roll like a conveyor belt? A leading interpretation of images taken of Saturn's most explosive moon indicate that they do. This form of asymmetric tectonic activity, very unusual on Earth, likely holds clues to the internal structure of Enceladus, which may contain subsurface seas where life might be able to develop. Pictured above is a composite of 28 images taken by the robotic Cassini spacecraft in 2008 just after swooping by the ice-spewing orb. Inspection of these images show clear tectonic displacements where large portions of the surface all appear to move all in one direction. On the image right appears one of the most prominent tectonic divides: Labtayt Sulci, a canyon about one kilometer deep. The magnitude of Enceladus' wobble as it orbits Saturn might indicate damping by a globally extending underground ocean layer.